¿Alguna vez se ha preguntado por qué algunos sistemas magnéticos parecen desafiar a la física? Se trata de lo siguiente: existe una disposición especial de imanes llamada matriz Halbach que crea un efecto casi mágico: hace que el campo magnético sea muy intenso en un lado y prácticamente lo elimina en el otro.
¿Cuál es el principio de la matriz Halbach? Es una configuración específica de imanes permanentes en la que cada imán gira 90 grados con respecto a su vecino, creando una interferencia constructiva en un lado y una interferencia destructiva en el otro. El resultado es un campo magnético concentrado casi el doble de potente que una disposición convencional de imanes en el lado activo.
En este puesto, como profesional Fabricante de matrices Halbach, Déjame que te lo explique.
Resumen rápido:
- Una matriz Halbach gira cada imán 90 grados respecto a su vecino, creando una interferencia constructiva que duplica la intensidad del campo en un lado y la anula en el otro.
- Construir uno requiere paciencia, ya que los imanes intentarán dar la vuelta - empieza con 5 imanes y utiliza un adhesivo fuerte o fijaciones.
- Elija matrices lineales para la fuerza direccional (maglev) o cilíndricas para la rotación (motores), pero prescinda de ellas si necesita la máxima fuerza de tracción hacia el acero o soluciones sencillas de bajo coste.
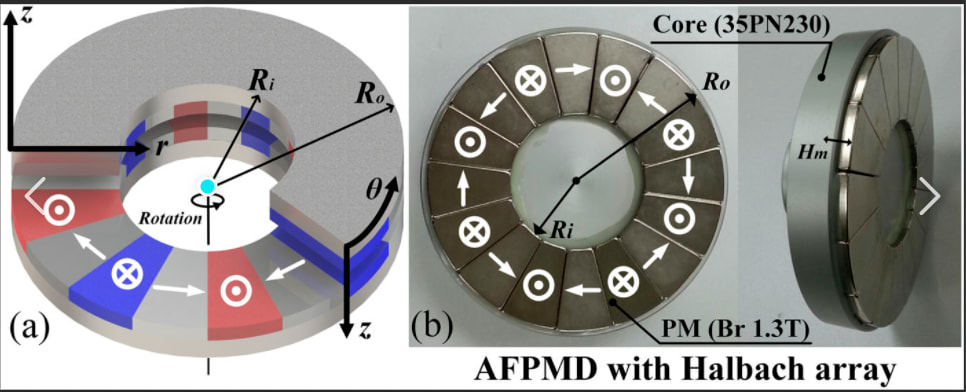
Física básica de las matrices Halbach
Piense en una matriz Halbach como en un equipo de imanes trabajando juntos en perfecta armonía.
Pero aquí está la cosa: en lugar de simplemente alinearlos como soldados, giras la orientación de cada imán 90 grados. Es como si cada imán diera un cuarto de vuelta en un baile coordinado.
¿El resultado? Superposición - los campos magnéticos se suman en un lado y se anulan en el otro.
Esto es lo que pasa:
- En el lado “fuerte”: las líneas de flujo magnético se alinean y refuerzan mutuamente
- En el lado “débil”: las líneas de flujo se oponen y anulan
- La intensidad de campo puede ser casi el doble que la de un imán estándar
He visto a ingenieros quedarse boquiabiertos cuando medían por primera vez la diferencia de campo entre los dos lados. Es así de espectacular.
Cómo la rotación de 90 grados crea la magia
La salsa secreta está en ese cuarto de vuelta de rotación entre imanes adyacentes.
En una disposición normal de imanes, los apilarías de norte a sur. Simple, ¿verdad? Pero en una matriz Halbach, estás creando un patrón vectorial magnético giratorio.
Imagina esta secuencia:
- Primer imán: Polo norte hacia arriba
- Segundo imán: Polo norte hacia la derecha
- Tercer imán: Polo norte hacia abajo
- Cuarto imán: Polo norte hacia la izquierda
- Quinto imán: Polo norte hacia arriba (el ciclo se repite)
Esto crea lo que los físicos llaman un “patrón de magnetización sinusoidal”. Las ondas magnéticas se suman literalmente en un lado mediante interferencia constructiva.
Consejo profesional: Cuantos más imanes se añaden a la matriz, más pronunciado es el efecto. He probado matrices con 5 imanes frente a 20 imanes: la diferencia es notable.
Aplicaciones reales que le dejarán boquiabierto
Hablemos de dónde aparecen estas matrices en el mundo real.
Trenes Maglev
En Inductrack utiliza matrices Halbach para hacer levitar trenes de varias toneladas. Una vez en movimiento, el tren no necesita energía. Las matrices crean un campo tan potente que pueden soportar 50 veces su propio peso.
Motores eléctricos
“Los motores ”sin hierro“ o ”sin núcleo" utilizan conjuntos cilíndricos Halbach. ¿Cuál es el resultado? Motores con:
- Mayor relación par-peso
- Mayor eficiencia (hasta 95% en algunos diseños)
- Menor generación de calor
La puerta de su frigorífico
Sí, esos imanes flexibles de nevera utilizan un patrón Halbach básico. ¿Alguna vez has notado cómo se adhieren firmemente a la nevera pero apenas atraen nada desde el frente? Eso es una matriz de Halbach en funcionamiento.
Aceleradores de partículas
Aquí es donde Klaus Halbach desarrolló originalmente el concepto en la década de 1980. Estas matrices enfocan haces de electrones con una precisión increíble.
La base matemática (simplificada)
Sé que las matemáticas pueden hacer que a la gente se le pongan los ojos chiribitas. Pero quédate conmigo un segundo.
La intensidad del campo magnético en un conjunto Halbach ideal sigue esta relación:
- La intensidad de campo disminuye exponencialmente en el lado débil
- La intensidad de campo aumenta exponencialmente en el lado fuerte
- La transición se produce en el plano de los imanes
Para los amantes de los detalles técnicos: el campo puede describirse mediante B = B₀ * e^(kz), donde k está relacionado con el periodo espacial del conjunto.
Pero esto es lo que realmente importa: el campo en el lado fuerte puede ser de 1,5 a 2 veces mayor que el de un imán convencional.
Construya su propio conjunto Halbach: Paso a paso
¿Quieres comprobarlo por ti mismo? A continuación te mostramos cómo construir una sencilla matriz lineal:
- Obtener imanes para cubos (cubos de neodimio de 1/2 pulgada funcionan muy bien)
- Marcar los postes claramente en cada imán
- Fijar el primer imán con el Norte hacia arriba
- Gire cada imán subsiguiente 90 grados en el sentido de las agujas del reloj
- Utilice un adhesivo fuerte o un soporte no magnético
Advertencia: Estos imanes intentarán girar y atraerse de formas no deseadas. Construir un conjunto Halbach requiere paciencia y, a veces, un accesorio para mantenerlos en su sitio.
Personalmente, recomiendo empezar con sólo 5 imanes. Una vez que le cojas el truco, aumenta la escala.
Matrices cilíndricas frente a matrices lineales: ¿Cuál necesita?
No todas las matrices Halbach son iguales. Los dos tipos principales tienen fines distintos:
Matrices lineales
- Utilizado en: Sistemas maglev, cintas transportadoras
- Ventaja: Crea un campo magnético itinerante
- Ideal para: Aplicaciones que necesitan fuerza direccional
Matrices cilíndricas
- Utilizado en: Motores, generadores, cojinetes magnéticos
- Ventaja: Crea una concentración de campo radial
- Ideal para: Maquinaria rotativa
Esto es lo esencial: Elija en función de si necesita movimiento lineal o rotativo.
Errores comunes sobre las matrices Halbach
Permítanme aclarar una confusión que veo a menudo.
Idea errónea #1: “Las matrices Halbach crean energía gratuita”
La realidad: Sólo son más eficientes en dirigir los campos magnéticos existentes. No se rompe ninguna ley física.
Idea errónea #2: “Imanes más grandes siempre significan matrices más fuertes”
La realidad: El patrón de rotación importa más que el tamaño. He visto imanes grandes mal dispuestos superados por matrices pequeñas bien diseñadas.
Idea errónea #3: “Siempre son la opción más fuerte”
La realidad: Para la fuerza de atracción pura al acero, otras configuraciones podrían ganar. Los conjuntos Halbach son excelentes para crear campos intensos en el espacio libre.
Consideraciones de diseño avanzadas
Cuando estés listo para ir más allá de lo básico, ten en cuenta estos factores:
Uniformidad de campo
El campo magnético no es perfectamente uniforme en el lado fuerte. Hay ligeras variaciones que siguen un patrón sinusoidal. En aplicaciones de precisión, hay que tenerlo en cuenta.
Efectos de borde
Las matrices no se extienden infinitamente. El campo disminuye en los bordes. La mayoría de los diseños lo compensan con “imanes de protección” en los extremos.
Estabilidad térmica
Los imanes de neodimio pierden fuerza a altas temperaturas. Para aplicaciones de alta temperatura, considere imanes de samario-cobalto en su lugar.
Costes de material
Un conjunto Halbach utiliza más material magnético que un diseño sencillo. Pero el aumento de rendimiento suele justificar el coste.
He trabajado en proyectos en los que el cambio a una matriz Halbach redujo el peso total del sistema en 40% manteniendo la misma intensidad de campo.
El futuro de la tecnología Halbach Array
Las aplicaciones siguen ampliándose. Esto es lo que hay en el horizonte:
- Transferencia inalámbrica de energía sistemas que utilizan matrices Halbach para mejorar la eficacia
- Productos sanitarios con campos magnéticos controlados con precisión
- Propulsión espacial sistemas que utilizan las matrices para enfocar los haces de iones
- Almacenamiento de energía volantes con cojinetes magnéticos
La tecnología que empezó como una “curiosidad” en 1973 es ahora esencial para la ingeniería de vanguardia.
Optimización del diseño del conjunto Halbach
¿Quieres el máximo rendimiento? He aquí las principales estrategias de optimización:
- Coincidir con la longitud de onda a su solicitud
- Utilizar imanes de alta calidad (neodimio N52 para temperatura ambiente)
- Minimizar lagunas entre imanes
- Considere la segmentación para matrices grandes
- Modelo antes de construir mediante análisis de elementos finitos
Recuerde: incluso pequeñas mejoras en la disposición pueden suponer un aumento significativo de la intensidad de campo.
Resolución de problemas comunes de las matrices Halbach
Cuando las cosas van mal, esto es lo que hay que comprobar:
Problema: Campo débil en el lado “fuerte
- Compruebe la orientación de los imanes (un solo imán incorrecto arruina el efecto).
- Verificar el grado y la fuerza del imán
- Buscar segmentos desmagnetizados
Problema: Dificultades de montaje
- Utilizar fijaciones no magnéticas
- Considerar segmentos modulares
- Trabaje primero con submatrices más pequeñas
Problema: Falta de uniformidad del campo
- Añade más imanes para suavizar las variaciones
- Ajuste la separación entre imanes
- Considere una longitud de onda diferente
La elección correcta para su aplicación
Entonces, ¿cuándo hay que utilizar una matriz Halbach?
Utilízalos cuando los necesites:
- Máxima intensidad de campo con el mínimo peso
- Concentración de campo unilateral
- Campos parásitos reducidos
- Mayor eficiencia de los motores/generadores
Sáltatelos cuando lo necesites:
- Fuerza máxima de tracción al acero
- Soluciones sencillas y económicas
- Campos uniformes en grandes superficies
Lo esencial
¿Cuál es el principio de la disposición de Halbach? Es la forma que tiene la naturaleza de demostrarnos que la disposición inteligente vence a la fuerza bruta. Al girar cada imán 90 grados en secuencia, creamos una interferencia constructiva que concentra drásticamente el campo magnético donde queremos.
Las aplicaciones van desde los imanes de la nevera hasta los trenes que levitan. Y a medida que avanzamos hacia 2026 y más allá, siguen apareciendo nuevas aplicaciones en campos como las energías renovables y la tecnología espacial.
La belleza de la matriz Halbach reside en su elegante simplicidad: sólo imanes dispuestos en un patrón específico, pero capaces de distribuciones de campo magnético aparentemente imposibles. Una vez que entiendas el principio, empezarás a ver oportunidades para aplicar esta magia magnética en todas partes.



