Ever wondered how industries separate iron from other materials at scale?
Here’s the thing:
The magnetic drum separator working principle is actually pretty straightforward once you break it down. And in this guide, as a professional magnetic drum manufacturer, I’m going to show you exactly how these machines work, step by step.
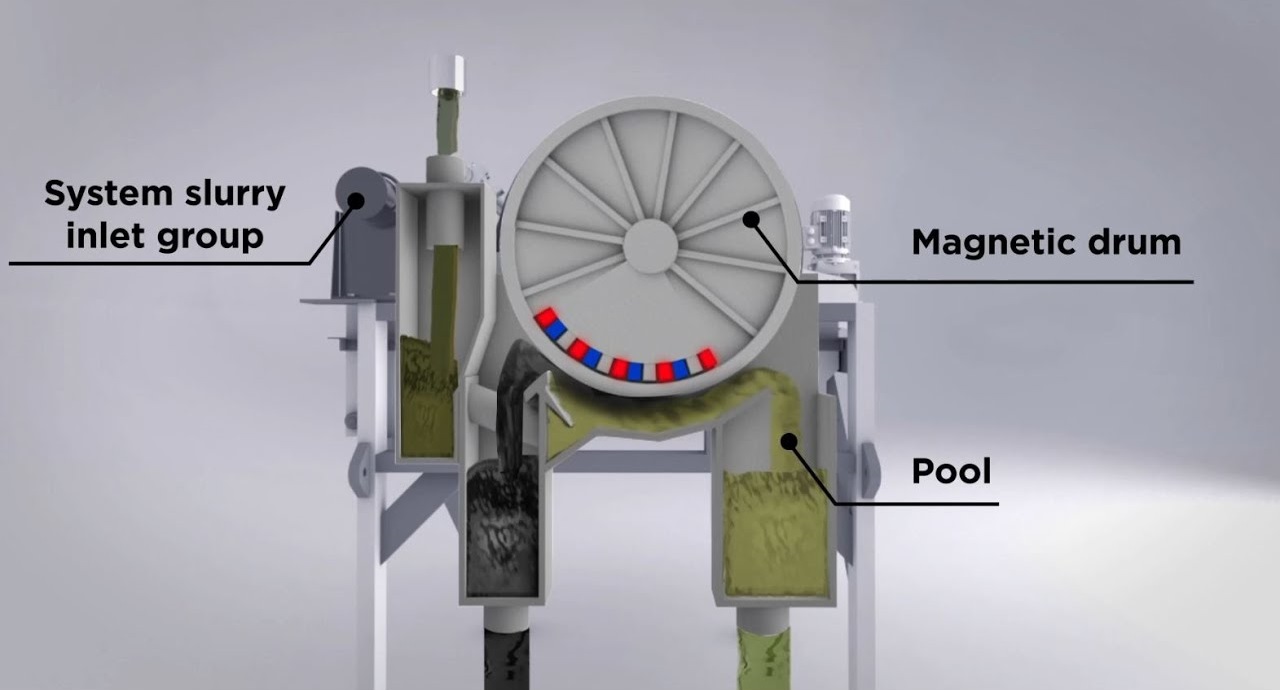
Table of Contents
What Is a Magnetic Drum Separator?
A magnetic drum separator is basically a rotating cylinder with powerful magnets inside that pulls ferrous materials away from non-magnetic particles.
Think of it like a super-powered magnet on steroids.
But here’s where it gets interesting:
These machines can process TONS of material per hour. And they do it continuously, without stopping.
Pretty cool, right?
How Does a Magnetic Drum Separator Work?
Let me break down the exact process for you.
Step 1: Material Feeding
First, your mixed material enters the separator.
This could be:
- Crushed ore from a mine
- Recycled materials on a conveyor belt
- Grain or food products
- Industrial waste
The material gets fed onto the top of the rotating drum (or sometimes underneath, depending on the setup).
Step 2: The Magnetic Field Does Its Thing
Here’s where the magic happens.
Inside the drum, there’s a stationary magnetic assembly. This creates a powerful magnetic field across part of the drum’s surface – usually about 180 degrees worth.
And when I say powerful, I mean it. Some of these magnets can generate fields up to 2.2 Tesla. That’s SUPER strong.
Step 3: Separation Occurs
As the drum rotates, two things happen:
- Ferrous materials (like iron and steel) get attracted to the drum and stick to it
- Non-magnetic materials just fall away due to gravity
It’s that simple.
The magnetic particles literally cling to the drum’s surface while everything else drops into a separate collection area.
Step 4: Discharge
Now here’s the clever part:
As the drum keeps rotating, those magnetic particles get carried PAST the magnetic field. Once they’re outside the field’s influence, gravity takes over and they fall into their own collection chute.
The result? You’ve got two separate streams: magnetic and non-magnetic materials.
Types of Magnetic Drum Separators
Not all drum separators are created equal. Let me show you the main types you’ll encounter.
Wet Drum Separators
These bad boys work in slurry or liquid environments.
They’re perfect for:
- Mining operations dealing with ore slurries
- Processing fine magnetic particles
- Situations where you’re already working with wet materials
The big advantage? They can capture REALLY fine particles that dry separators might miss.
Dry Drum Separators
On the flip side, dry drum separators handle materials without any liquid involved.
They’re ideal for:
- Recycling facilities
- Bulk material handling
- Situations where adding water isn’t practical
Pro tip: Dry separators typically have lower operating costs since you don’t need water handling systems.
Key Components That Make It All Work
Let’s dive into what’s actually inside these machines.
The Drum Shell
This is usually made from non-magnetic stainless steel. Why? Because you don’t want the drum itself becoming magnetic – that would mess everything up.
The diameter can range from 12 inches to several feet, depending on your application.
The Magnetic Assembly
This is the heart of the system.
You’ve got two main options:
- Permanent magnets (usually rare earth magnets)
- Electromagnets
Most modern systems use permanent magnets because:
- No electricity required
- More reliable
- Lower operating costs
The Drive System
A motor rotates the drum at a specific speed – usually between 15-40 RPM.
Too fast and materials don’t have time to separate properly. Too slow and you’re killing your throughput.
Feed and Discharge Systems
These ensure materials flow smoothly through the separator.
Good design here makes the difference between 90% efficiency and 99% efficiency.
Real-World Applications
So where do you actually see these machines in action?
Mining and Mineral Processing
This is the big one.
Mining operations use drum separators to:
- Extract magnetite from ore
- Remove tramp iron before crushers
- Upgrade ore quality
- Recover valuable magnetic minerals
I’ve seen operations that process thousands of tons per day with these machines.
Recycling Industry
Recycling facilities are ALL about magnetic separation.
They use it for:
- Pulling steel from shredded cars
- Cleaning up electronic waste
- Separating metals from municipal waste
- Processing construction debris
Food and Grain Processing
Here’s one that might surprise you:
Food processors use magnetic drum separators to remove tiny metal contaminants from:
- Flour
- Sugar
- Spices
- Grain products
It’s a critical safety step that prevents metal fragments from ending up in food products.
Factors That Affect Separation Efficiency
Not getting the results you want? Here are the main factors to consider.
Magnetic Field Strength
This is obvious but crucial.
Stronger magnetic fields = better capture of weakly magnetic materials.
But here’s the thing: More isn’t always better. You need the RIGHT strength for your specific material.
Drum Speed
Like I mentioned earlier, speed matters.
Too fast and particles don’t have time to be attracted. Too slow and you’re wasting capacity.
Most operations find their sweet spot through testing.
Feed Rate
Overload the separator and efficiency drops fast.
The material needs to form a thin layer on the drum for optimal separation. Pile it on too thick and magnetic particles get buried under non-magnetic ones.
Particle Size
Smaller particles are harder to capture than larger ones.
Why? Physics. Smaller particles have less mass for the magnetic force to act on.
That’s why wet separators often work better for fine materials – the liquid helps control the particles.
Advantages of Magnetic Drum Separators
Let me tell you why these machines are so popular.
Continuous Operation
Unlike batch processes, drum separators run 24/7.
No stopping to clean. No downtime between batches. Just continuous separation.
High Capacity
A single drum can handle massive amounts of material.
I’m talking hundreds of tons per hour for large industrial units.
Low Operating Costs
Especially with permanent magnet systems, operating costs are minimal.
No electricity for the magnets. Just power for the drum rotation.
Simple Maintenance
These machines are workhorses.
Regular maintenance basically involves:
- Checking bearings
- Inspecting the drum surface
- Occasional belt replacement (if applicable)
That’s it.
Common Problems and Solutions
Even the best equipment has issues sometimes. Here’s what to watch for.
Reduced Separation Efficiency
Problem: Not capturing as much magnetic material as before.
Solutions:
- Check magnet strength (magnets can weaken over time)
- Clean the drum surface
- Verify proper drum speed
- Check feed rate isn’t too high
Excessive Wear
Problem: Drum surface wearing out faster than expected.
Solutions:
- Add wear-resistant coating
- Check for abrasive materials in feed
- Ensure proper material distribution
Material Buildup
Problem: Materials sticking where they shouldn’t.
Solutions:
- Install cleaning brushes or scrapers
- Adjust magnetic field configuration
- Check moisture content (for dry separators)
Choosing the Right Separator
So how do you pick the right one for your operation?
Start with these questions:
- What’s your material? (Size, magnetic properties, moisture content)
- What’s your capacity requirement? (Tons per hour)
- Wet or dry process?
- What’s your target separation efficiency?
- What’s your budget? (Initial cost AND operating costs)
Pro tip: Always test your actual material before buying. What works great for one operation might not work for another, even with similar materials.
Future Trends in Magnetic Drum Separation
The technology keeps evolving. Here’s what’s coming:
Stronger Magnets
Rare earth magnet technology continues to improve. We’re seeing stronger fields in smaller packages.
Smart Controls
Modern separators include:
- Automated monitoring systems
- Variable speed controls
- Real-time efficiency tracking
- Predictive maintenance alerts
Hybrid Systems
Combining multiple separation technologies in one unit for better overall recovery.
Bottom Line
The magnetic drum separator working principle is elegantly simple: use magnetic force to attract and separate ferrous materials from non-magnetic ones through a rotating drum system.
But while the principle is simple, the execution requires careful attention to details like magnetic field strength, drum speed, and feed rates.
Whether you’re in mining, recycling, or food processing, understanding how these machines work helps you optimize your separation processes and get better results.
And remember: The best separator in the world won’t help if it’s not matched to your specific application. Take the time to analyze your needs, test your materials, and choose accordingly.
The magnetic drum separator working principle has been proven effective across countless industries for decades, and with modern improvements in magnet technology and control systems, these workhorses are only getting better.



