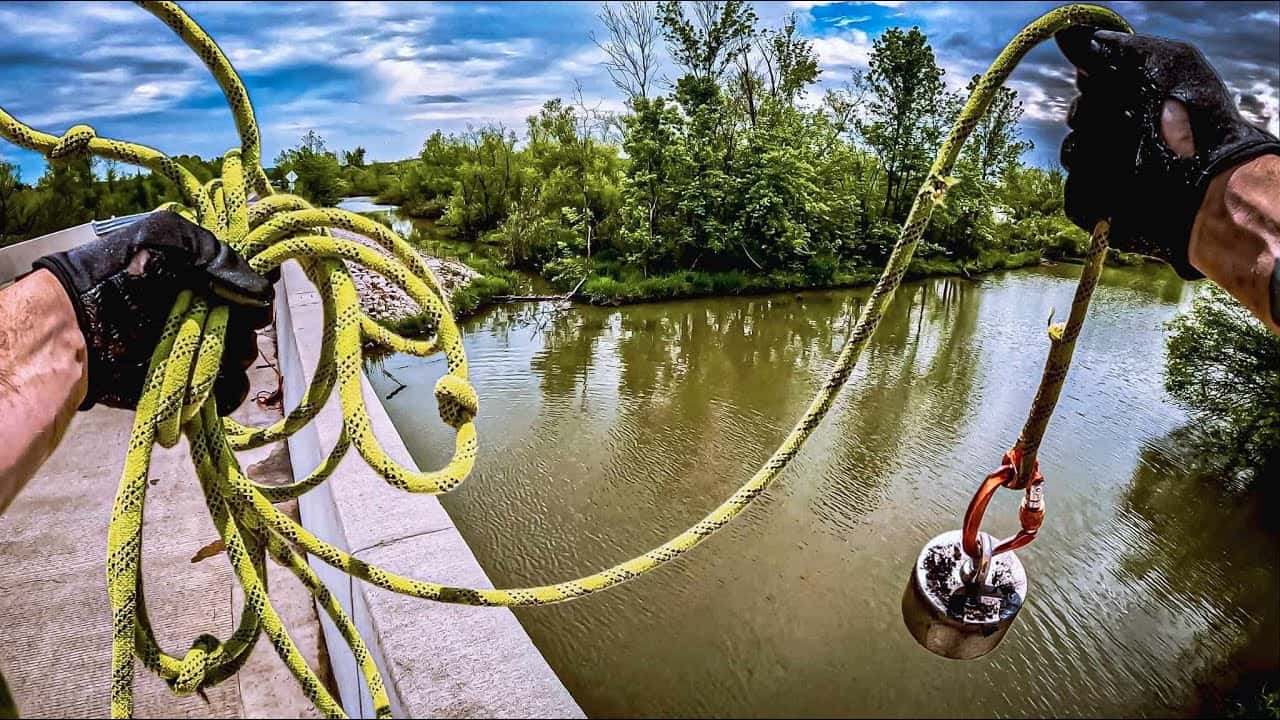
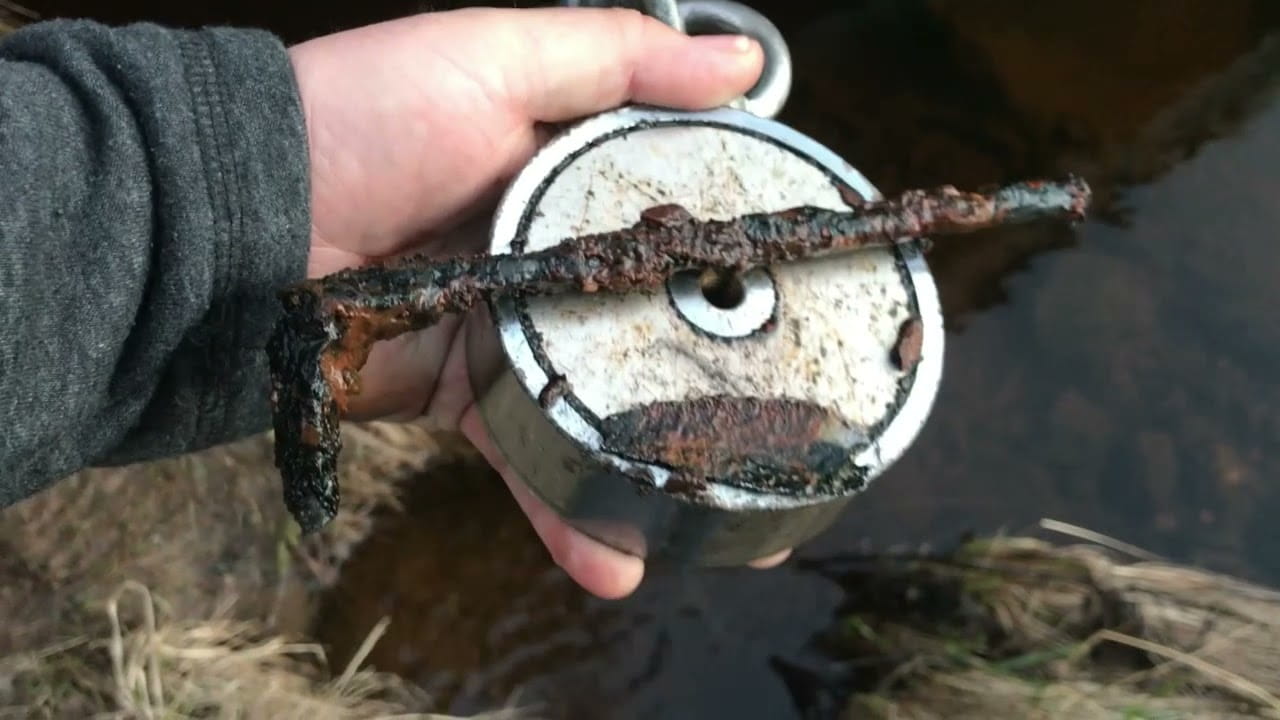
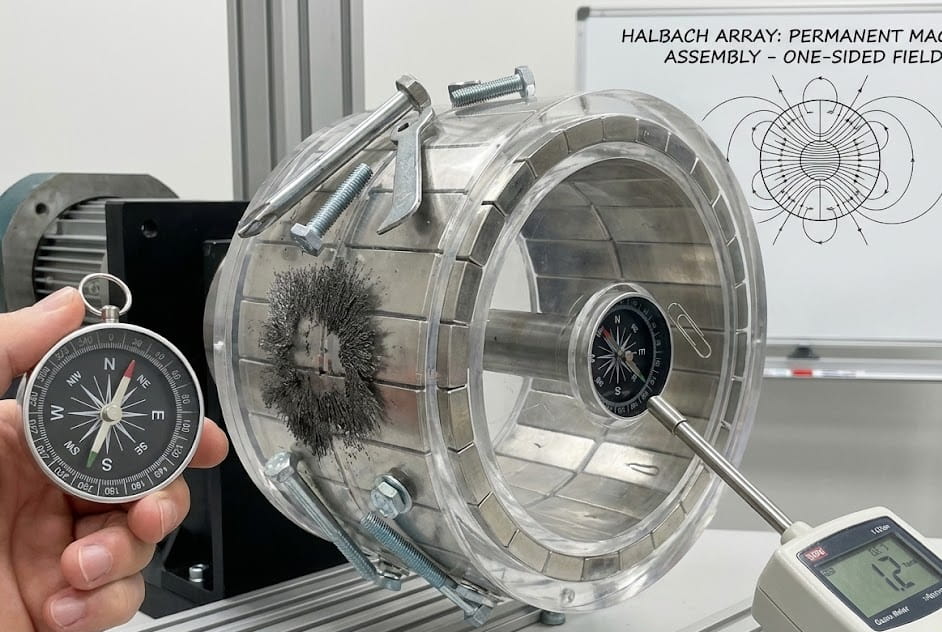
What Magnet for Magnet Fishing: Complete Selection Guide
Discover what magnet for magnet fishing actually works. Learn why neodymium magnets are essential, recommended pull strengths by experience level, and avoid costly mistakes with our tested recommendations.
What Magnet for Magnet Fishing: Complete Selection Guide Read More »