Ever wondered how industries keep their products free from pesky metal contaminants? Or how mining operations sort valuable minerals from waste? Here’s the deal: it all boils down to the magnetic separator working principle. This tech uses magnetic fields to pull apart materials based on their magnetic properties. In this guide, as a professional magnetic drum manufacturer, I’ll break it down step by step, so you can understand exactly how magnetic separators work – and why they’re game-changers in fields like recycling and manufacturing.
Let me explain why this matters. Magnetic separators aren’t just gadgets; they’re essential tools that boost efficiency and safety. Whether you’re in food processing or mineral extraction, grasping the magnetic separator working principle can help you optimize operations. Sound good? Let’s dive in.
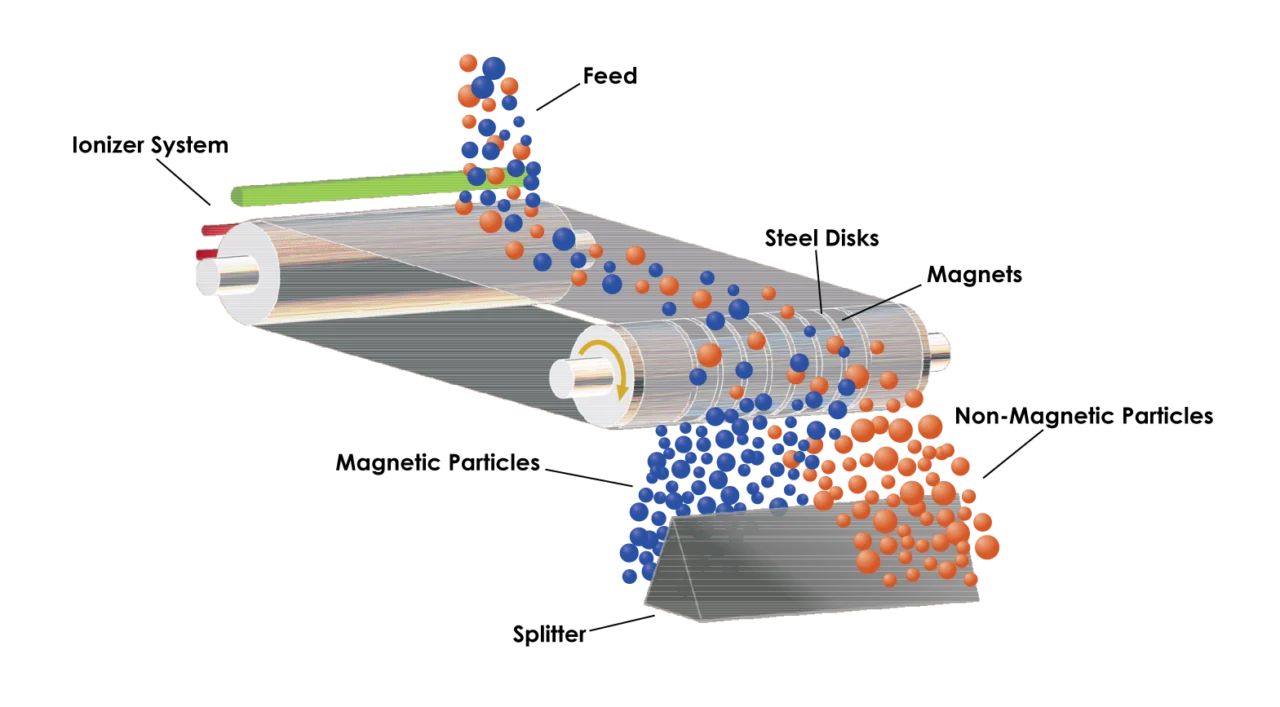
Table des matières
Qu'est-ce qu'un séparateur magnétique ?
First things first: a magnetic separator is a device that sorts materials by exploiting differences in magnetic properties. Think of it as a magnet on steroids, designed to attract and capture ferrous (magnetic) particles from a mix, leaving non-magnetic stuff behind.
In my experience, these separators come in handy across tons of industries. For example, in recycling plants, they pull out iron scraps from waste streams. Or in food production, they snag metal bits that could contaminate products. Without them, you’d have equipment breakdowns or safety hazards left and right.
But here’s the thing: not all magnetic separators are created equal. Some use permanent magnets, while others rely on electromagnets for adjustable strength. The key? They all hinge on the same core idea – magnetic attraction.
Principe de fonctionnement du séparateur magnétique à noyau
Okay, let’s get to the heart of it. The magnetic separator working principle relies on magnetic fields to influence materials differently based on their susceptibility.
Here’s a simple breakdown:
Materials fall into three categories when exposed to a magnetic field:
- Ferromagnetic: Strongly attracted (like iron or nickel). These are easy to separate.
- Paramagnetic: Weakly attracted (think aluminum or platinum). Needs a stronger field.
- Diamagnetic: Slightly repelled (such as gold or quartz). These pass through unaffected.
The process kicks off with a magnetic field generated by magnets inside the separator. As your mixture – whether it’s dry powder, slurry, or bulk material – flows through, magnetic particles stick to the magnet or get diverted.
Non-magnetic bits? They keep moving along their path.
Pro Tip: Always match the field’s intensity to your materials. Too weak, and you miss contaminants; too strong, and you waste energy.
In practice, this principle powers continuous operations. For instance, in a drum separator, the drum rotates, picking up magnetic stuff on its surface while non-magnetics fall away. It’s efficient and hands-off.
Étape par étape : Comment fonctionne la procédure de séparation ?
Want a clear picture? I’ll walk you through the magnetic separation process like I would if nous were chatting over coffee.
Step 1: Generate the Magnetic Field. This is where permanent magnets or electromagnets create the force. Electromagnets let you tweak the strength – super useful for varying materials.
Step 2: Feed the Material. Dump your mixture in via conveyor, chute, or pipe. Consistency is key here; uneven flow can mess up separation.
Step 3: Attraction and Diversion. As stuff passes the field, magnetic particles get pulled toward the magnet. It’s like an invisible hand grabbing them. Non-magnetics? They sail right by.
Step 4: Collection. Magnetic material gets scraped off or released into a bin. Non-magnetics go to another. In continuous setups, like overband magnets, this happens non-stop.
But here’s the bottom line: the magnetic separator working principle isn’t magic – it’s physics. The force equation? F = B * (dB/dx) * V * χ, where B is field strength, V is particle volume, and χ is susceptibility. Don’t worry if that’s Greek to you; just know stronger fields mean better pulls.
In my view, testing is crucial. I’ve seen setups fail because the field wasn’t calibrated right. Run trials with your specific mix to nail it.
Types de séparateurs magnétiques et application du principe
Not every separator works the same. Different designs tweak the magnetic separator working principle for specific jobs.
Let’s list out the main types:
- Magnetic Drum Separators: A rotating drum with internal magnets. As material passes over, magnetics stick to the shell. Great for mineral processing, like separating iron ore. In action, the principle shines – continuous rotation keeps things moving.
- Overband Magnets: Hung over conveyors, these lift tramp iron from bulk flows. Mining loves them for protecting crushers. The working principle? Suspended magnets create a field that yanks metals upward.
- Eddy Current Separators: These use alternating fields to induce currents in non-ferrous metals, repelling them. Recycling pros – think sorting aluminum from plastic. It’s a twist on the basic principle, focusing on repulsion.
- Suspension and Conveyor Belt Separators: Similar to overbands but integrated into belts. Food industry staple for impurity removal.
Each type leverages the core principle differently. For example, eddy currents add a repulsive force for non-magnetics, expanding applications.
In 2025, with smarter tech, we’re seeing AI-tuned fields for even better efficiency. But the fundamentals? They stay the same.
Applications dans le monde réel : Les points forts de ce principe
Magnetic separators aren’t theoretical – they’re everywhere. Let’s look at some examples.
En l'exploitation minière et le traitement des minerais, Ils extraient les minerais de fer des scories. Une étude de cas : Une carrière a utilisé des séparateurs à tambour pour augmenter la pureté du minerai de 20%, réduisant ainsi les déchets.
Recyclage? Les modèles à courants de Foucault trient les métaux des déchets électroniques. Les statistiques montrent qu'ils récupèrent jusqu'à 95% de métaux non ferreux, selon les rapports de l'industrie.
Le alimentaire et pharmaceutique Les secteurs de l'agriculture et de la pêche comptent sur eux pour assurer leur sécurité. Imaginez un moulin à grains : les séparateurs enlèvent les clous ou les vis, évitant ainsi les rappels. FDA Les lignes directrices les imposent souvent.
Même en produits chimiques et plastiques, Ils purifient les matières premières. Une usine de plastique que je connais a réduit de moitié les défauts en ajoutant des séparateurs sur les convoyeurs.
Conseil de pro : Adaptez le type d'appareil à votre débit. Gros volume ? Optez pour le tambour. Précision ? Courant de Foucault.
Ces applications montrent le principe de fonctionnement du séparateur magnétique en action - en résolvant des problèmes réels avec la force magnétique.
Avantages et inconvénients à connaître
Aucune technologie n'est parfaite. Pesons le pour et le contre.
Avantages:
- Efficacité: Taux de séparation élevés, souvent 99% pour la ferromagnétique.
- Capacité: Traite d'énormes volumes - pensez à des tonnes par heure dans l'industrie minière.
- Récupération: Augmente les rendements, comme la récupération de la magnétite dans le traitement du minerai.
- Respect de l'environnement: Pas besoin de produits chimiques, juste des aimants.
Dans une étude, les séparateurs magnétiques ont permis de réduire la consommation d'énergie de 30% par rapport aux méthodes traditionnelles.
Inconvénients:
- Maintenance: Les aimants s'usent ; le nettoyage est une corvée.
- Limites: Faible sur les particules diamagnétiques ou fines.
- Coût: Investissement initial, en particulier pour les modèles à haute intensité.
- Faute: Des éléments non magnétiques peuvent s'accumuler, ce qui réduit l'efficacité.
La clé ? Un entretien régulier. D'après mon expérience, la programmation de nettoyages permet d'éviter la plupart des problèmes.
Conseils de pro pour optimiser votre séparateur magnétique
Prêt pour la mise en œuvre ? Voici des conseils pratiques.
- Testez votre matériel: Effectuer des tests de susceptibilité. Des outils tels que les gaussmètres permettent d'évaluer les besoins sur le terrain.
- Étalonnage régulier: Les champs s'affaiblissent avec le temps. Vérifier tous les mois.
- Intégrer intelligemment: Associer à des cribles ou des concasseurs pour un meilleur débit.
- Contrôler les performances: Utiliser des capteurs pour obtenir des données en temps réel. En 2025, l'IdO facilitera cette tâche.
- Choisir le bon type: Ne forcez pas un tambour dans un travail de boue - optez pour un séparateur humide.
Une petite histoire : Un client souffrait d'un faible taux de récupération. Nous avons opté pour un modèle à courants de Foucault, et boum - 15% de remontée. De petits ajustements, de grandes victoires.
Les erreurs courantes à éviter
J'ai vu des gens trébucher ici. Ne le faites pas.
- Ignorer la taille des particules: Trop fin ? Gouttes de séparation. Pré-écran.
- Surcharge: Dépasse la capacité, efficacité des réservoirs.
- Skipping Maintenance: Leads to failures. Set reminders.
- Wrong Field Strength: Test first.
Avoid these, and your setup will hum.
Tendances futures en matière de séparation magnétique
Looking ahead to 2025 and beyond, things are evolving.
AI integration? It’s coming – auto-adjusting fields based on feed.
Superconducting magnets? Stronger fields, lower energy.
Hybrid systems? Combining with optical sorters for ultimate purity.
Stats predict the market hits $1.5 billion by 2025, driven by recycling demands.
Stay ahead by watching these.
Conclusion : Maîtriser le principe de fonctionnement du séparateur magnétique
There you have it – a deep dive into the magnetic separator working principle. From basics to advanced tips, this tech is all about harnessing magnetic fields for smart separation. Whether boosting efficiency or ensuring safety, it’s a powerhouse.
Remember: thorough testing and maintenance are your best friends. Apply this, and you’ll see results. Questions? Drop them below. Now go optimize that process!



